Marsyas the satyr, or silen, was seen as a mythological founder of aulos playing or a divine judge of it by the ancient Greeks. The way in which his aulos playing enraptured his audience was likened to the way in which Socrates mesmerised his audience with his philosophising words, and the fact that the two were both quite ugly is also picked up on in Plato's Symposium. For some time, Marsyas held a prominent position within the minds of the ancient Greeks, particularly the Athenians. There are many mentions of him within the textual record, and various fine examples of Athenian artisanship represent him, such as the statue group by Myron that would have sat atop the Acropolis.
The standard myth of Marsyas involves him picking up the auloi (plural of aulos) cast down by Athena. Athena threw down the auloi, so Melanippides relates, because she saw her reflection in a mirror as she played, and she thought that her puffed out cheeks were inelegant and unbecoming, though Telestes argued against this:
...somebody said that Melanippides, in his Marsyas, disparaging the art of playing the flute, had said very cleverly about Minerva:—
Athena cast away those instruments
Down from her sacred hand; and said, in scorn,
"Away, you shameful things—you stains of the body!
Shall I now yield myself to such malpractices'"And some one, replying to him, said,—But Telestes of Selinus, in opposition to Melanippides, says in his Argo (and it is of Athena that he too is speaking):—
It seems to me a scarcely credible thing
That the wise Pallas, holiest of goddesses,
Should in the mountain groves have taken up
That clever instrument, and then again
Thrown it away, fearing to draw her mouth
Into an unseemly shape, to be a glory
To the nymph-born, noisy monster Marsyas.
For how should chaste Athena be so anxious
About her beauty, when the Fates had given her
A childless, husbandless virginity? (Ath. 616e ff.)
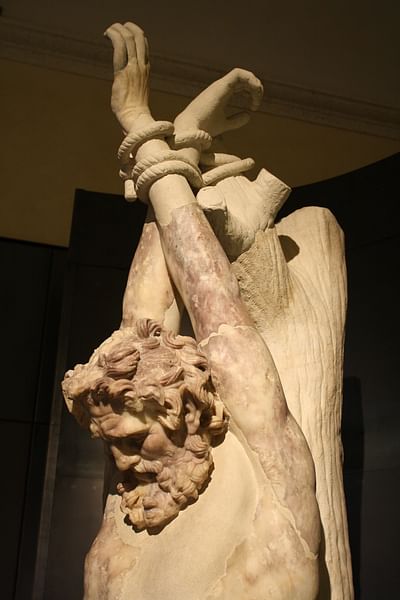
The satyr Marsyas picked up Athena's auloi, however, and at some point challenged Apollo to a contest (agon in the Greek). Apollo chose to play the lyre and, either through skill alone or a certain degree of trickery, beat Marsyas. Marsyas' punishment for thinking that he could out skill an Olympian was that he was hung up and skinned alive. The story of Marsyas has often been discussed within the context of New Music in Athens. A good example of this is the passages of Melanippides and Telestes preserved in Athanaeus which seemingly argue different corners in support of the aulos. However, due to Marsyas thinking himself superior to Apollo, it is a myth that is also used as an example of the dangers of hubris.
Marsyas also held appeal in Hellenistic and Roman times, but the focus becomes less on his agon with Apollo, or his picking up of the auloi from Athena, and more specifically on his punishment at the hands of Apollo. This can be seen clearly in a changing interest in iconographies of Marsyas, which show interest in depicting the flaying of Marsyas. We also know that a statue of Marsyas resided in the Roman forum (Horace S.1.6), and our surviving statues of Myron's Athenian group are in fact later Roman copies.
Various mythological genealogies were applied to Marsyas; he is often said to have been the son of an elder Olympus, sometimes of Hyagnis, or of Oeagrus. He was also said to have taught a younger Olympus (who was variably also recorded as Marsyas' son), who was famous for his music making, how to play the aulos.
Marsyas could also refer to a river in Phrygia named after the famous satyr. This part of the myth is recounted in Herodotus 7.26, Xenophon Anabasis 1.2, referred to at Plato Euthyd. 285d, and beautifully retold by Ovid, Metamorphoses 6.382, where the tears of Marsyas' companions collect in the river, another example of the Roman interest in the flaying of Marsyas:
The Satyr Marsyas, when he played the flute
in rivalry against Apollo's lyre,
lost that audacious contest and, alas!
His life was forfeit; for, they had agreed
the one who lost should be the victor's prey.
And, as Apollo punished him, he cried,
“Ah-h-h! why are you now tearing me apart?
A flute has not the value of my life!”Even as he shrieked out in his agony,
his living skin was ripped off from his limbs,
till his whole body was a flaming wound,
with nerves and veins and viscera exposed.But all the weeping people of that land,
and all the Fauns and Sylvan Deities,
and all the Satyrs, and Olympus, his
loved pupil—even then renowned in song,
and all the Nymphs, lamented his sad fate;
and all the shepherds, roaming on the hills,
lamented as they tended fleecy flocks.And all those falling tears, on fruitful Earth,
descended to her deepest veins, as drip
the moistening dews,—and, gathering as a fount,
turned upward from her secret-winding caves,
to issue, sparkling, in the sun-kissed air,
the clearest river in the land of Phrygia,—
through which it swiftly flows between steep banks
down to the sea: and, therefore, from his name,
'Tis called “The Marsyas” to this very day.












